 |
| Key of School Solutions |
Class 10th geography || Unit 1 Physical Geography Questions Answers pdf download ||
TEXTUAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Q. No 9- 16
Ans
9. What is abrasion? What are the
features formed due to abrasion?
Ans. The desert winds may sometimes be very forceful. When such forceful winds blow, the sharp-edged sands and dust particles carried by them may erode the rock surfaces found in the way, by sheer friction. This is known as abrasion. As a result of abrasion, various features are formed in the desert and semi-desert areas. Due to continued abrasion over a considerable long period, the soft and least resistant rocks get eroded and are entirely worn away. But the hard rocks with high resistance become smooth and polished to a great extent and assume many shapes. The process of abrasion is responsible for the formation of inselberg, yardang, and other kinds of erosional features in the deserts.
10. Define attrition.
Ans. Attrition is one of the
processes of wind erosion in the desert. In this process, the sand and rock
particles are broken into smaller pieces through their mutual collision while
being carried by high velocity winds in deserts.
11. What are glaciers? What is the reason for their slow movement?
Ans. The extensive masses of ice which move very slowly over the land surface as sheets or move linearly through the mountain valleys downwards due to the gravitational force of the earth are known as glaciers. In general, glaciers mean the large masses of ice and snow on mountains, that move very slowly down a valley.
One of the chief characteristics
of glaciers is that they move very slowly mainly due to their vast size. In
fact, the speed of glaciers is affected by their size, the nature of the slope
and configuration of the surface of the mountain and the atmospheric
temperature. Therefore, huge blocks of ice move very slowly while smaller
pieces of ice move at a faster rate.
12. What are
the different types of glaciers? Write briefly about each of them.
Ans. Glaciers are huge blocks of
ice and snow which move very slowly over the land surface or move along the
mountain slopes downwards due to the gravitational force of the earth. On the
basis of location and nature, glaciers are mainly classified into three types :
(i) Continental glaciers: Continental glaciers are extensive ice sheets that cover the polar regions. The most striking feature of such glaciers is that they move very slowly due to their sheer size and low surface gradient of the polar regions. The continental glaciers can be seen in Northern Canada, Greenland, Scandinavia, Antarctic region, etc.
(ii) Mountain glaciers: Mountain glaciers originate in the high-altitude regions of the mountains. They are also called Alpine or Valley glaciers. This type of glaciers are found in the Alpe of Europe, the Rockies of North America and in the Himalayas of Asia. Such glaciers move comparatively faster then the continental glaciers.
(iii) Piedmont glaciers: The glaciers that are formed due to convergence of several mountain glaciers at the foothill zone are known as piedmont glaciers. Since these glaciers originate in the piedmont zone of the mountains, they are called piedmont glaciers. Such glaciers are common in Alaska of North America.
Elective Geography Class 10 Seba Question Answer English Medium
13. Draw a figure to show the
shape of a glacier valley.
Ans.
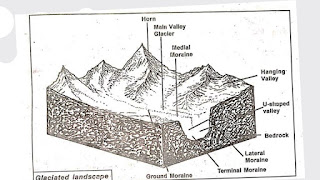 |
| shape of a glacier valley |
Ans. Hanging valley is one of the
erosional features created by glaciers. When a huge glacier moves down a
mountainous region, it create a large, wide of deep valley in the process. But
the region may have smaller glaciers which contribute to the main glacier. Such
tributary glaciers also create smaller, narrower, and less deep valleys. When
the tributary glaciers meet the main glacier, they appear to be hanging over
the main glacier. Therefore, the valleys created by the tributary glaciers also
appear to be hanging. Hence, such valleys are called hanging valleys. When
water falls vertically from the hanging valley to the main glaciers, waterfalls
are formed.
15. What are moraines? What are
their different types? Show the location of different moraines with the help of
a figure.
Ans. Moraines are the long ridges
of deposit or till of glacial debris or sediments such as rock pieces, clay,
sand and boulders which have been transported by a valley glacier along with
the ice. The moraines are the depositional features of a glacier which bring
about major changes on the earth's surface.
Moraines are basically of the
following four types: -
Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Notes
(i) Lateral moraine:
Lateral moraine is a ridge of glacial debris which are formed along the sides
parallel to the glacial valleys, i.e. these moraines lie on either side of a
glacier valley between the ice and steep sides of a glacier.
(ii) Ground moraine: The
moraines which move along the bottom bed of the glacier valley are known as
ground moraines. These are formed as a result of the deposition of sediments by
a valley glacier which while moving rapidly fails to carry the sediment load
and begins to leave an irregular sheet or till over the channel bed.
(iii) Medial moraine: when two glaciers join at a particular spot in the valley. Their lateral moraines also unite together and start flowing downward in the centre of the valley glacier valley. The moraines that move along the middle course of the glacier are known as medial moraines.
(iv) Terminal moraine:
Terminal moraine or end moraine marks the ultimate limit of an ice sheet or
glacier and is formed at the snout of the glacier, from where it starts
melting. Terminal moraine is actually a ridge formed by the deposition of
sediments carried down by a glacier which gets accumulated at the end of a
valley glacier. It consists of large angular boulders.
Elective Geography Class 10 Seba Question Answer English Medium
16. Based on
your general knowledge, state how global warming may have its various effects
on glaciers.
Ans. The
increase in global temperatures brought about by the increased emission of
greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide,
chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) water vapour, etc. into the atmosphere is known as
global warming. Global warming means an increase over a period of the average
temperature of earth's atmosphere and oceans. The greenhouse effect is
attributed to be the main reason for this phenomenon.
One of the negative impacts of global warming is that it may greatly
affect glaciers of the polar regions as well as those of the high mountain
ranges of the world. It may lead to the unnatural melting of glaciers resulting
in several changes in the landforms of the polar and mountainous regions. It
has been proved that the polar ice is beginning to melt mainly due to the high
rate of global warming leading to rising level of sea water. This can cause
floods, destruction of marine life and
thus upset the existing ecological balance. Similarly, currently there
is a view that the Himalayan snow may also melt sooner than expected. Such a
situation in the near future will have serious repercussions particularly in
the Indian subcontinent leading to the drying of perennial rivers which water
the northern and northern-eastern plains •of India. The melting of such ideal
sources of fresh water will have disastrous consequences. Glaciers are the best
sources of fresh water and therefore their melting can deplete freshwater
resources in the world to a great extent and thereby affect the very existence
of terrestrial life on earth.
******
Elective Geography Class 10 Seba Question Answer Chapter 1 ||
Click here to download free pdf question Answer





0 Comments